Set 4 | Important Ecology MCQs
Important Ecology MCQs. Ecology plays a crucial role within the broader field of environment and ecology. It serves as a foundational concept for achieving success in competitive exams such as Civil Services, State exams, SSC, Railways, Banking, and more. Mastering these subjects offers a unique advantage, allowing you to gain invaluable insights into the country’s environmental legacy. With a focus on Environment, Biodiversity, and Ecology, this knowledge not only sharpens your competitive edge but also equips you to excel in these challenging exams.
| MCQs on Ecology – Objective Questions and Answers |

Q31. Which of the following constitute a food chain? (Chhattisgarh P.C.S. (Pre) 2016)
[A] Grass, wheat and mango
[B] Grass, goat and human
[C] Goat, cow and elephant
[D] Grass, fish and goat
[E] None of the above
View Explanation
Correct Answer is B.
In the food chain consisting of grass, goat, and humans, the sequence is as follows:
- Grass (Autotroph)
- Goat (Herbivorous Consumer)
- Humans (Omnivorous Consumer)

Q32. The pyramid of energy in any ecosystem is (M.P.P.C.S. (Pre) 2020)
[A] Always upright
[B] May be upright and inverted
[C] Always inverted
[D] None of the above
View Explanation
Correct Answer is A.
- The pyramid of energy is always upright and cannot be inverted because energy is lost as heat at each step of the trophic levels. Each bar in the energy pyramid represents the amount of energy available at each trophic level over a specific period, such as annually, per unit area.
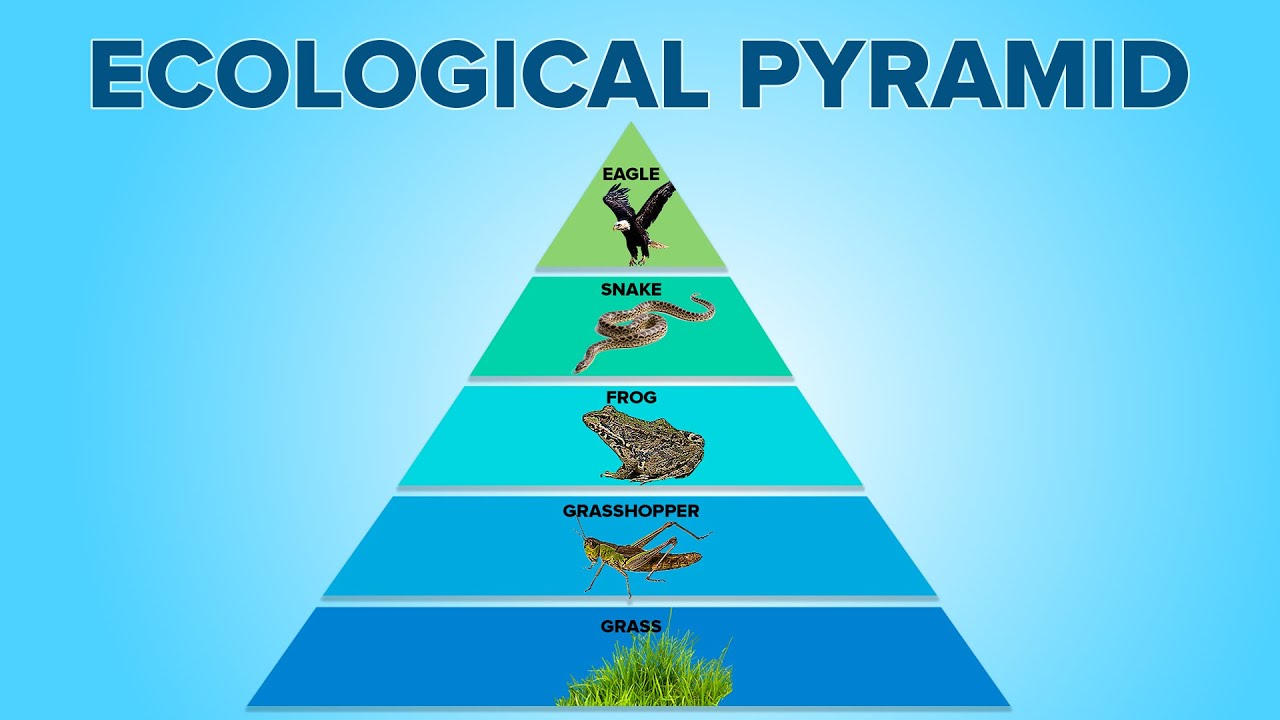
Q33. Biomass Pyramid is reversed in which type of ecosystem? (U.P.P.S.C. (GIC) 2010)
[A] Forest
[B] Pond
[C] Grassland
[D] Drylands
View Explanation
Correct Answer is B.
- The Pyramid of Biomass graphically represents the amount of biomass per unit area at different trophic levels within an ecosystem.
- In grasslands and forests, there is a gradual decrease in biomass from producers to top carnivores, resulting in an upright pyramid. However, in a pond ecosystem, where producers are small organisms with relatively low biomass, the biomass increases up the food chain. This leads to an inverted pyramid shape, with greater biomass at higher trophic levels.
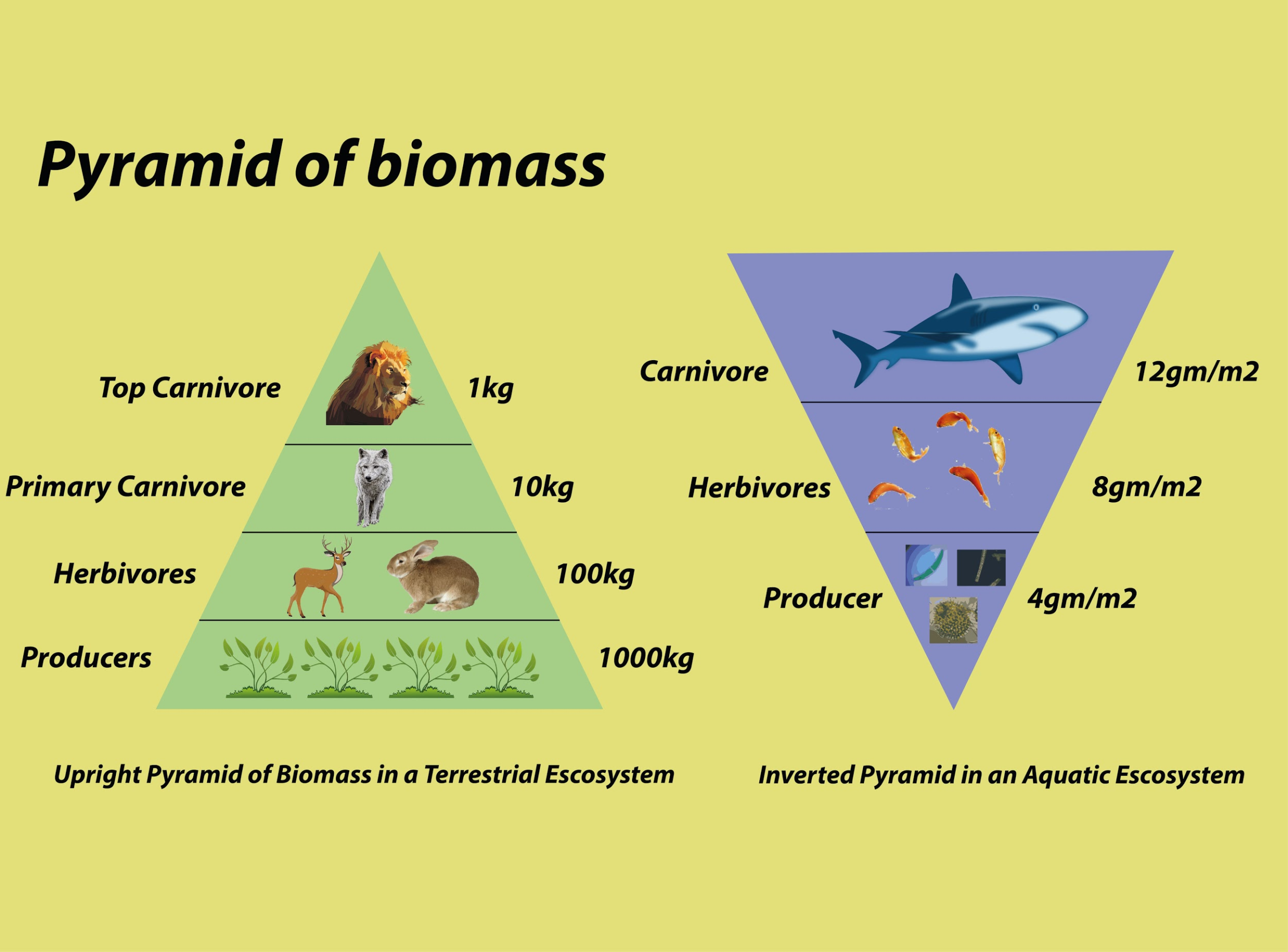
Q34. An inverted pyramid of biomass can be found in which ecosystem? (R.A.S./R.T.S. (Pre) 2021)
[A] Marine
[B] Grassland
[C] Forest
[D] Tundra
View Explanation
Correct Answer is A.
- An inverted pyramid of biomass is commonly found in marine ecosystems. This occurs because the biomass of fish and other consumers significantly exceeds that of phytoplankton, which are the primary producers.
- Despite their low biomass, phytoplankton reproduce rapidly and sustain the higher trophic levels, leading to an inverted biomass pyramid.

Q35. Which one of the following organisms is likely to show the highest concentration of DDT, once it has been introduced into the ecosystem? (I.A.S. (Pre) 1997)
[A] Grasshopper
[B] Toad
[C] Snake
[D] Cattle
View Explanation
Correct Answer is C.
- DDT is a non-biodegradable pollutant that biomagnifies, meaning its concentration increases as it moves up the food chain from producers to tertiary consumers.
- In the given example, since the snake represents the tertiary consumer, it will have the highest concentration of DDT compared to producers, primary consumers, and secondary consumers.
Q36. The amount of energy during the transfer from one trophic level to another in an eco-system- (U.P. R.O./A.R.O. (Pre), 2017)
[A] Increases
[B] Decreases
[C] Remains constant
[D] May increase or decrease
View Explanation
Correct Answer is B.
- Energy is the basic force responsible for all metabolic activities. The flow of energy from producer to top consumers is called energy flow, which is unidirectional. Energy flows through the trophic levels i.e. from producers to subsequent trophic levels.
- This energy always flows from lower (producer) to higher (herbivore, carnivore, etc.) trophic level. There is a loss of some energy in the form of unusable heat at each trophic level so the amount of energy during the transfer from one trophic level to another decreases in an ecosystem.
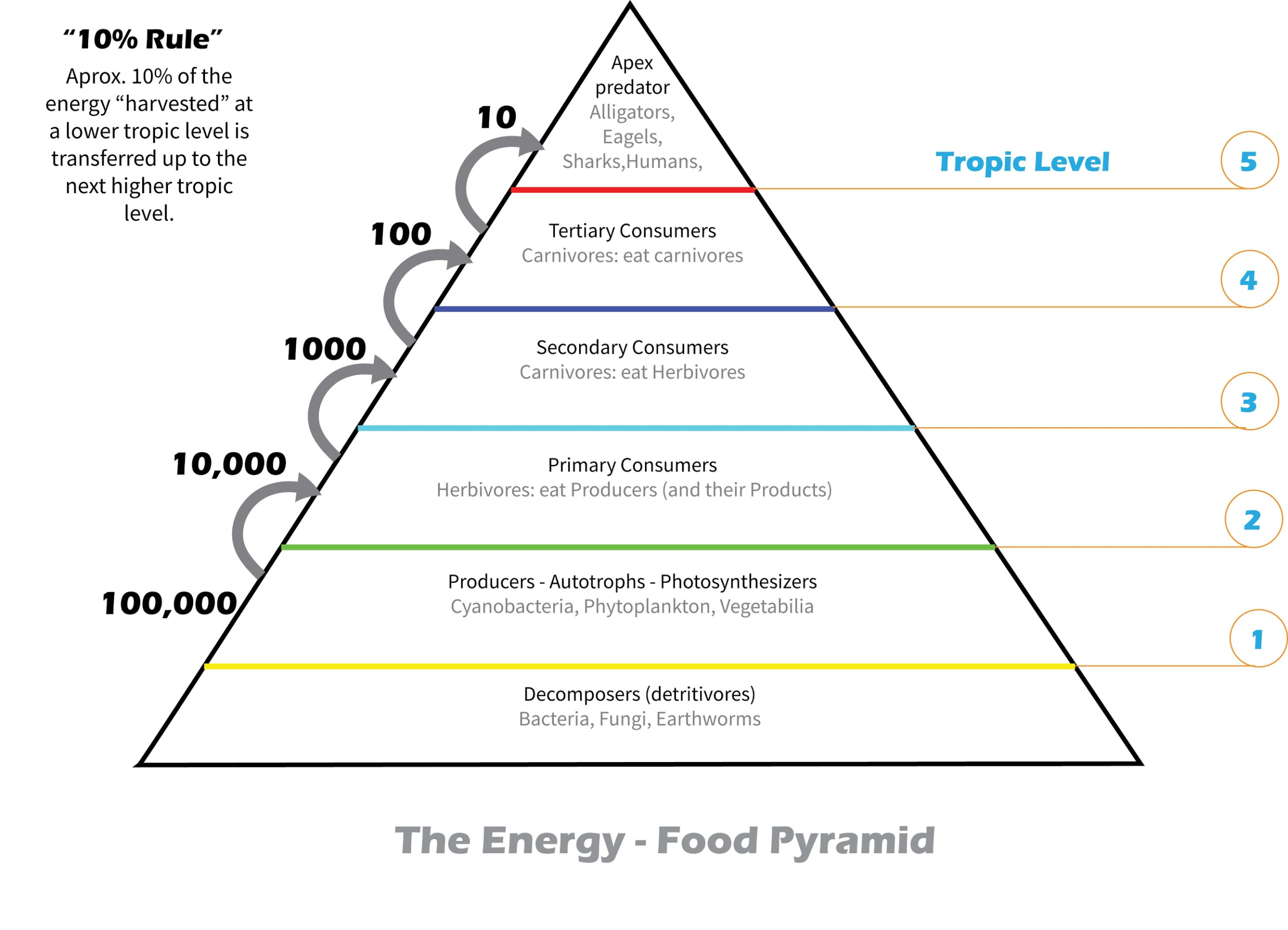
Q37. The amount of energy during transfer from one trophic level to another in an ecosystem– (U.P.P.C.S. (Pre) 2019)
[A] Increases
[B] Decreases
[C] Remains constant
[D] May increase or decrease
View Explanation
Correct Answer is B.
- Energy always flows from lower (producer) to higher (herbivore, carnivore, etc.) trophic level. There is a loss of some energy in the form of unusable heat at each trophic level so the amount of energy during the transfer from one trophic level to another decreases in an ecosystem.

Q38. Which one of the following trees is not eco-friendly? (U.P.P.C.S. (Mains) 2011)
[A] Babul
[B] Eucalyptus
[C] Neem
[D] Pipal
View Explanation
Correct Answer is B.
- Eucalyptus trees consume more groundwater than many other tree species, which can lead to a decrease in water levels in areas where they are planted. This characteristic has earned them the reputation of being detrimental to the environment. Eucalyptus trees are predominantly found in Australia, where their high water usage can significantly impact local water resources.
Q39. Which one of the following trees is considered to be an environmental hazard? (U.P.P.C.S. (Pre) 2005)
[A] Babul
[B] Amaltas
[C] Neem
[D] Eucalyptus
View Explanation
Correct Answer is D.
- Eucalyptus trees consume more groundwater than many other tree species, which can lead to a decrease in water levels in areas where they are planted. This characteristic has earned them the reputation of being detrimental to the environment. Eucalyptus trees are predominantly found in Australia, where their high water usage can significantly impact local water resources.

Q40. The example of “Lentic Habitat” in the freshwater community is: (MP.P.C.S. (Pre) 2014)
[A] Ponds and swamps
[B] Waterfalls and rivers
[C] Ponds and rivers
[D] All the above.
View Explanation
Correct Answer is A.
- Lentic Ecosystem: These are characterized by still or slow-moving water bodies. Key features include:
- Habitats: Ponds, lakes, swamps, marshes, and reservoirs.
- Water Flow: Minimal or no current; water is relatively stagnant.
- Biota: Often includes algae, aquatic plants, fish, amphibians, and various invertebrates adapted to low-flow conditions.
- Nutrient Cycling: Nutrient levels can vary, and such ecosystems often experience stratification, where layers of water with different temperatures and oxygen levels form.
- Lotic Ecosystem: These are characterized by flowing water bodies. Key features include:
- Habitats: Rivers, streams, and creeks.
- Water Flow: Continuous movement of water, which creates current and turbulence.
- Biota: Species adapted to flowing conditions, such as certain fish, insects, and plants. Organisms may be streamlined or have adaptations to handle strong currents.
- Nutrient Cycling: Nutrient flow is more dynamic, and these ecosystems often have a more continuous exchange of materials with their surroundings.
Both types of ecosystems play crucial roles in their environments, supporting diverse species and contributing to the overall health of aquatic systems.





